
 Xingaonai
Xingaonai
Understanding the performance curve of the pump is crucial for the performance of the pump under specific conditions.
The pump performance curve is a very important parameter of the pump. It allows you to know the pump's head, water flow, power, efficiency and other performance parameters at a glance. Usually, the pump performance curve consists of two lines, one is the straight line corresponding to the maximum power of the motor, and the other is the straight line where the highest head and the best efficiency are located. The head refers to the resistance height that the pump needs to overcome when it sucks water out, the water flow refers to the amount of water flowing per hour, the efficiency refers to the conversion efficiency of the water pump, and the power refers to the required electrical energy consumed by the pump. In special cases, the pump performance curve may be discontinuous or faulted. By analyzing the curve, the various performance parameters of the pump can be determined.
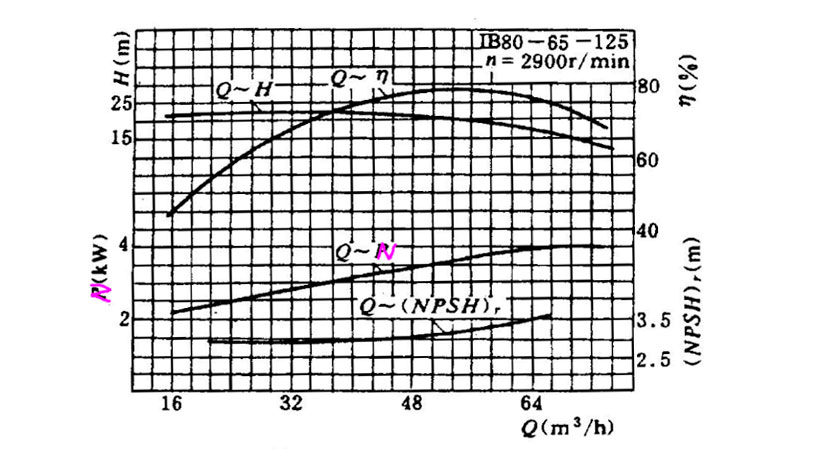
Generally, the flow rate Q is used as the horizontal coordinate, and the head H, power N, efficiency n and allowable suction vacuum Hs are used as the vertical coordinate to draw Q~H, Q~N, Q~n, Q~Hs curves.
1. Flow rate refers to the volume of liquid delivered by the pump during operation. It is the horizontal coordinate of the pump's performance curve. The flow rate is generally marked in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) or tons per hour (T/h).
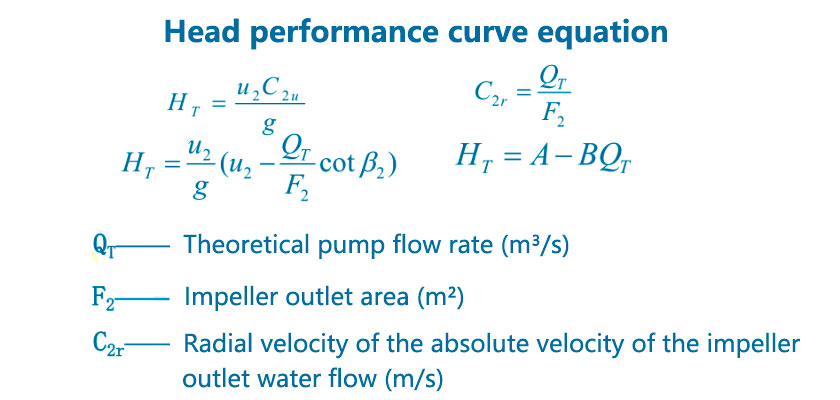
2. Head refers to the resistance that the pump has to overcome when delivering liquid. It is the vertical coordinate of the pump's performance curve. Usually, the head indicates the height at which the pump can provide water flow and is marked in meters (m).
3. Efficiency refers to the shape of the pump performance curve, and is also the conversion rate of the pump from mechanical energy and electrical energy to fluid energy. Generally, the highest efficiency of the pump is expressed as a percentage within a certain range of head and flow rate.
4. Power is the power required when the pump is running. Generally, it is the power required by the pump to drive the motor.
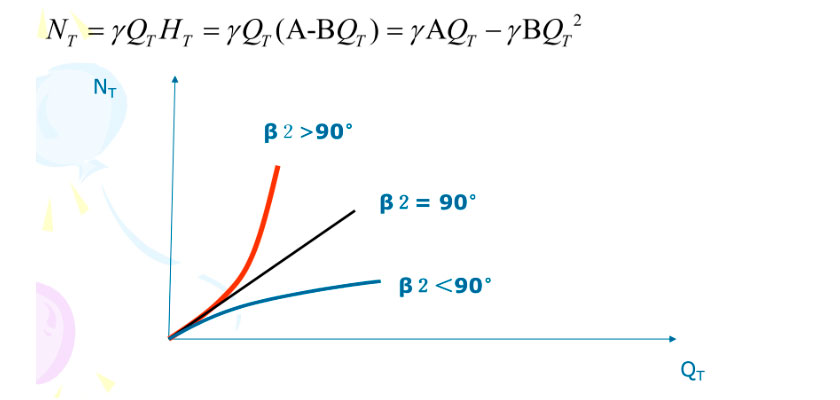
5. The rated point refers to the rated head and rated flow of the pump. A rated point marked on the curve is also the rated performance parameter when the pump is designed, the optimal working point.
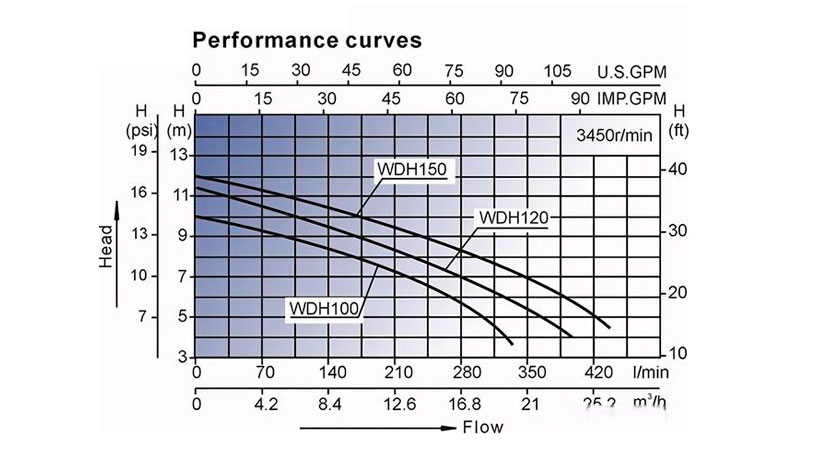
6. The working point refers to the head and flow of the pump in actual work. The appropriate working point can maximize the efficiency of the pump.
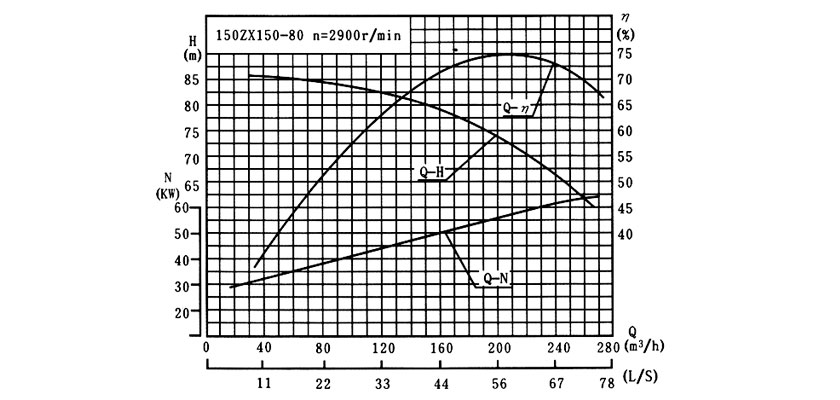
Before using the pump, we need to understand the actual situation, the pipeline system and the water flow operating conditions, and then analyze the appropriate working point according to the performance curve. When selecting the working point according to the curve, we also need to calculate the pressure loss of the pipeline and the connected equipment, that is, the actual head value. The performance curves of different manufacturers and different models will also be very different. We also need to analyze according to the performance curves of different pumps and finally choose the appropriate pump. In the actual use process, it is necessary to monitor the changes in the performance curve of the pump in real time, which can effectively understand the work and health of the pump, and timely repair it when problems occur to ensure the maximum efficiency of the pump.
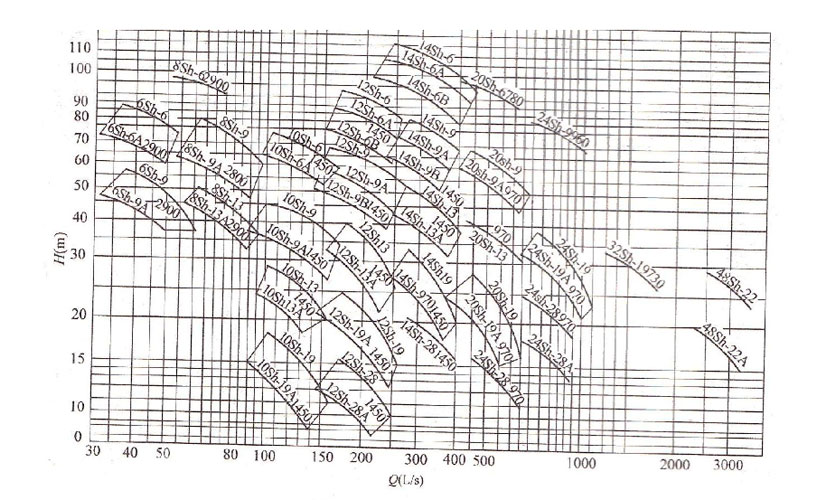
In general, the pump performance curve is an important indicator for monitoring the performance and health of the pump. By analyzing the best working point on the curve, the efficiency and life of the pump can be improved. Finally, I hope that everyone can better understand the performance curve of the pump through this article and use the working efficiency of the pump better.
Superior: No content!
Abajo: No content!
Nuestros productos se han exportado a más de 170 países de África, Asia, América del Sur, Europa, etc. Estamos aquí para ofrecerle mejores productos y servicios.
Copyright © 2024-2030 Xingaonai Group Todos los derechos reservados. Sitemap